Did you know the first MOOC (Massive Open Online Course) was released in 2006?
Over a decade later, many things have changed including courses becoming shorter and deadlines becoming more flexible.
Recently, the Metaverse and VR (virtual reality) have been used in a couple of interesting Metaverse MOOC case studies and a new one with the Vili project is just about to start.

Credit: Rawpixel.com – Freepik.com
Vili’s Metaverse MOOC
The ViLi Project has carried out research into how educators are currently using visual technologies in their teaching practice. The Metaverse MOOC is on ‘Visual Literacies: Exploring Educational Practices and Technologies’ and shares what they have found out from leading practitioners using exciting new practices and technologies such as virtual reality.
The project has partnered with MootUp to bring a ground-breaking experience to participants. This is the world’s first Metaverse MOOC.
This Metaverse MOOC is exploring many new technologies like holograms, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR) and mixed reality (XR) so this is an exciting opportunity to see VR in action during these lessons and discussions.
The Vili project features a 3D auditorium with a large stage, many seats and a lot of space to add extra content!
And because this is delivered using HTML5 and WebXR there is nothing to install, and 100% audience access is guaranteed, all an attendee needs is a web browser. Anyone can join on smartphone, tablet, laptop, desktop or immersively using any VR headset.
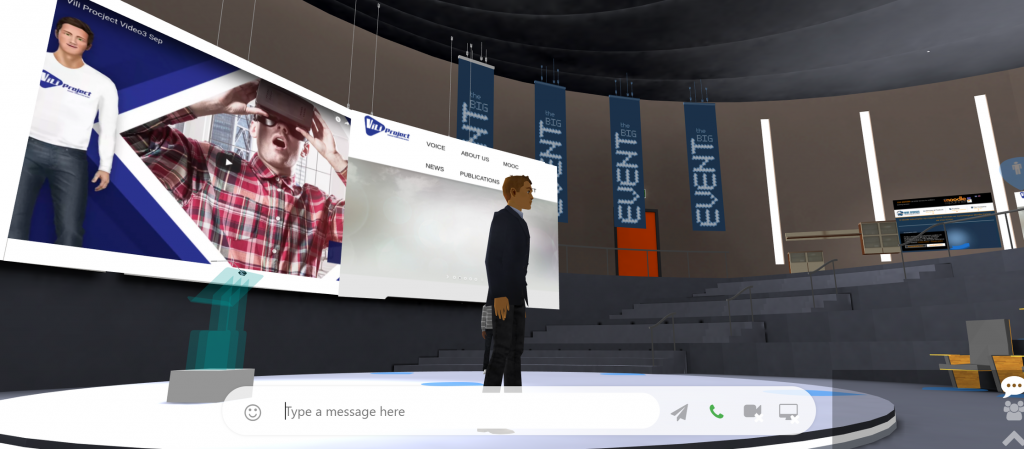
The MootUp Metaverse platform is a VR-ready online 3D space authoring tool that allows instructional designers to build immersive learning experiences.
It offers a range of customizable 3D and 360 spaces in order to create visual experiences that are unique, memorable and captivating for your users.
Not only that, the 3D auditorium space offers a Social Metaverse as a unique benefit!
Social Metaverse
A social metaverse has the ability to socialise with others in VR.
In a social space, you can send messages, voice call, video chat or gesture.
This helps to break down the isolation barriers that often plague MOOCs and other long distance learning options.
You can use your avatar to present with audio, using tools like the laser pointer to draw students attention to specific parts of the scene/presentation/slides/images.
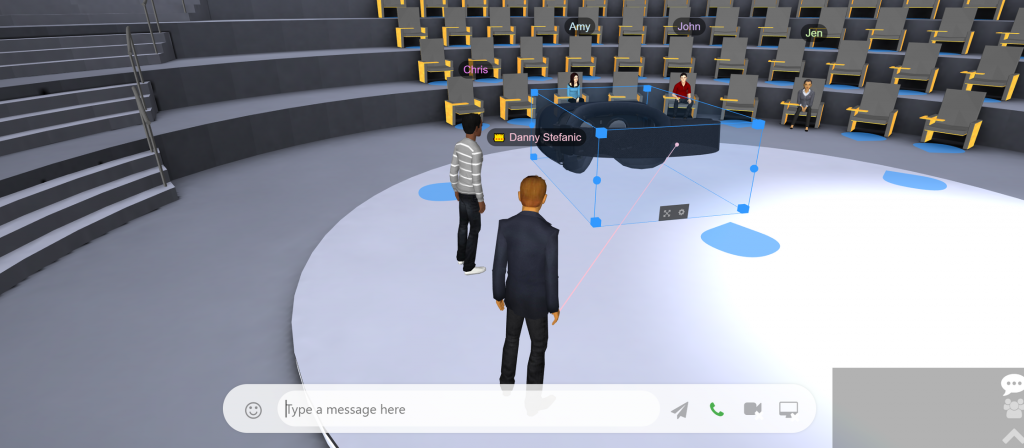
Enjoy a live session as an avatar with other students (like a college lecture) or with video conference. You can even project live video into VR, allowing you to present to your class as you would do with any other video conferencing software!
You can take interaction a step further by adding 3D items to the stage and using the laser pointer to point out specific things to participants (enabling an interactive style of teaching online).
How to create a Metaverse MOOC
Combining Vili’s existing MOOC with the MootUp Metaverse platform was simple to achieve by adding a single SCORM activity into the Vili Metaverse MOOC (Moodle LMS).
Each participant gets an avatar when they enter the VR activity. The avatar is automatically connected to their Metaverse MOOC user identity and any achievements or scores acquired in VR are passed back to the Metaverse MOOC for completion tracking or reports.
VR Headset or Not?
All of this can be simply put together to allow learners to experience the Metaverse MOOC in a 3D virtual-reality (VR) ready environment!
What’s VR-Ready? It means that it is ready for VR but that VR is not essential to make it run.
The course can be used by anyone, they can join in from their mobile, tablet, laptop, desktop if they don’t have access to VR goggles.
If they do have VR goggles, they can experience it all in VR using Oculus/Meta Quest, Microsoft Hololens, MagicLeap, Pico, HTC Vive or even legacy headsets such as Oculus Go or cardboard.
The growth of Metaverse MOOCs and VR
MOOC stands for Massive Open Online Courses.
These are huge courses that are available online and are open to (almost) everyone.
Students sign up for a course that is either self-paced (they work by themselves at whatever speed the need or like) or session-based (the course has start and end dates as well as deadlines for information) and work through the course’s content.
There are MOOCs available in a range of languages and in different fields, allowing materials to be opened up to more learners around the world.
Credit: Macrovector – Freepik.com
Some are free, some have a fee and others offer the option to pay (and gain a certificate) or to gain the knowledge for free (with no qualification).
Even though the “M” stands for “Massive”, class sizes differ substantially and the average has been changing over the years.
In 2014, researcher Katy Jordan found that there was an average of 43,000 students per MOOC but only 6.5% of them finished the course.
A year later, she found that average class sizes were decreasing but the rate of course completion was increasing: showing a more engaged and committed group of learners!
Despite average class sizes decreasing, It is still a big and growing market place.
By the end of 2016, 58 million students had signed up to at least one MOOC.
How quickly is the market growing?
The number of MOOCs available is growing year by year.
In 2014, there were roughly 1,000 available but in 2018, there were over 8,000!
Coursera saw a 70% increase in its paying customers in 2017. They also had 30 million people signed up to the platform and close to $100 million in annual revenue.
Not only that, but MOOCs are available in a wide range of fields (% of total MOOCs):
- Technology (19.9%) – Education & Teaching (8.5%)
- Business (18.5%) – Engineering: (7.1%)
- Social sciences (10.6%) – Art & Design: (5.5%)
- Science (10.0%) – Mathematics: (3.3%)
- Humanities (9.5%)
MOOCs are a great way to open up learning to a huge audience, but they are not a perfect teaching solution.

Credit: Freepik
Top 4 Challenges for MOOCs
MOOCs have a number of different problems and we are going to look at a few key ones:
#1 Isolation
Students log on from their own house or office which, on one hand, is very convenient and allows people to connect from all across the world.
On the other hand, it removes the usual communication and socialisation that you can experience at a course, leading to isolation.
Many MOOCs try to work around this by using messenger boards and chat rooms to let students talk to each other.
These can sometimes help, but they are often too big to offer actual support and assistance to students who are feeling lost in this huge, online world.
#2 No feedback
Courses are usually developed by professionals or professors of a given field, which means that there is a lot of great information in them.
However, students need to study alone and often get very little feedback.
This can also add to a student’s feeling of isolation (if your work or effort is ignored, you can feel utterly alone).
#3 Low motivation
Being alone in your studies can hit motivation hard.
Studying as an adult is difficult: you have to carve out time from your day in order to sit down and focus on learning new information.
Although you might have a goal in mind, it still requires energy on top of your normal schedule (with work, family, relationships, leisure etc).
Add in a lack of guidance or support with the course, motivation naturally declines.
#4 Low completion rates
Carrying on from low motivation, we move straight into low completion rates.
If you don’t want to study, you won’t study and then you won’t finish the course.
This means that you will not learn the skills you want or need to gain a qualification.
Low completion rate is a real problem with MOOCs: students start dropping out right from the first week.
Created by Katemangostar – Freepik.com
These four problems create real issues for the education business.
So what can be done to help combat them?
How can the Metaverse help with these challenges?
The Metaverse offers many positives that could be useful in targeting some of the difficulties MOOCs face.
The Metaverse is a way to immerse your users in a 3D world which is captivating.
Captivated learners are motivated learners!
Many students feel frustrated in learning the theory because it doesn’t connect with their real lives.
However, the Metaverse transports you directly into a realistic environment and immerses you in the experience.
Education is already using VR to train astronauts, the military and surgeons and the technology is growing further still.
It is a great way to get experience of a dangerous situation without any real danger: a surgery student can practise their operating their skills in a realistic game before starting on a real patient.
By letting them experience something more real (albeit virtual), really helps motivation and learning.
At the same time, it can help eliminate isolation.
If you create a multi-user metaverse meeting room, students can come together into a virtual space with other students.
Even being sent into a metaverse auditorium can make a huge difference: you mentally step out of your living room and into a college campus!
Learning scenarios can be built to offer feedback or tell students when they make errors so that they can learn and try again.
All of these can help motivate students to continue studying and, therefore, combat low completion rates!
Therefore, the Metaverse could be a great way to eliminate some of the downsides of MOOCs.
Created by Freepik
What examples of Metaverse MOOCs are currently available?
Pairing the Metaverse with MOOCs is still relatively new so there are still only a few examples.
In 2016, Harvard took a big leap and taught one of their most popular MOOCs in VR.
All the lectures were shot by a 360° camera allowing them to be shown in virtual reality.
The reviews were extremely positive with users saying “CS50 is fantastic”,
“It’s a cultural touchstone, a lifestyle, a spectacle,” and even YouTube CEO Susan Wojcicki said CS50 changed her life.
This year, at Serious Play, UB (University at Buffalo) showed how they are using VR in a collaborative robot safety MOOC.
Organizers suggest that this might become a blueprint for colleges and university who want to use the Metaverse in their own online courses.
These are great stories demonstrating how the Metaverse has been used in MOOCs to date.
However, existing MOOCs utilizing VR have only employed 360 video training materials, enabling a participant to watch a presentation and look around. This helps increase engagement, but does not attempt to offer interactive experiences where the learner can impact the outcome, nor social VR experiences where learners can work together.
The Vili Metaverse MOOC includes these new levels of VR interaction. We invite you to take a look for yourself and join the Metaverse MOOC for free.

